Image

Personal
Personal
Personal
Personal
Discover how protecting biodiversity helps ensure thriving ecosystems that underpin the well-being of millions of people.
Find out more

Biodiversity provides us with our water, food, medicines, and ultimately affects our survival. Let's protect it to help ensure a sustainable future.


See how different species interact and influence
one another in fascinating ways.


At MSIG, we seek to contribute to the development of a vibrant society and help secure a sound future for the planet, by enabling safety and peace of mind. As an insurance company that sees the heart in everything, we recognise protecting biodiversity is fundamental to thriving ecosystems because they provide us with vital resources like food, water, and medicines. These are key to ensuring sustainable societies, and our existence.


Watch and discover how protecting biodiversity helps insure a sustainable future.


At MSIG, we partnered Conservation International Asia-Pacific (CIAP) to protect biodiversity by supporting the conservation of forests and oceans. The investment supported natural climate solutions. Nature provides 30% of the solution to mitigating climate change by helping to remove or avoid carbon emissions.
Learn more













Protecting large scale ecosystems is the insurance that this planet needs to reduce our risk of catastrophic loss. An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscapes, interact. The whole surface of Earth is a series of interconnected ecosystems. The more diverse the ecosystem, the more productive it is.
Click on each ecosystem to discover more.
Forests are among the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. Tropical rainforests are home to more species than any other terrestrial habitat and they are all interconnected with one another - whether for food, growth, survival, and more.
For example:
Forests provide homes for animals.
Some of these animals eat plants.
The plants need healthy soil to grow.
Fungi help decompose organic matter to fertilise the soil.
Here we see how the forest, Sunda pangolin, and termites are interconnected, as well as how forests affect humankind.
Forests are not only key to the flora and fauna species that dwell within, but are also important to human well-being. Healthy forests reduce the disastrous effects of both floods and droughts as they regulate the flow of water to downstream towns and cities. In addition, as many as 120 prescription drugs worldwide are derived directly from plants found in forests. Trees also mitigate the greenhouse gas effect by trapping heat and releasing life-giving oxygen. Protecting forests protects biodiversity, which influences every breath we take, every drop we drink and every bite we eat.
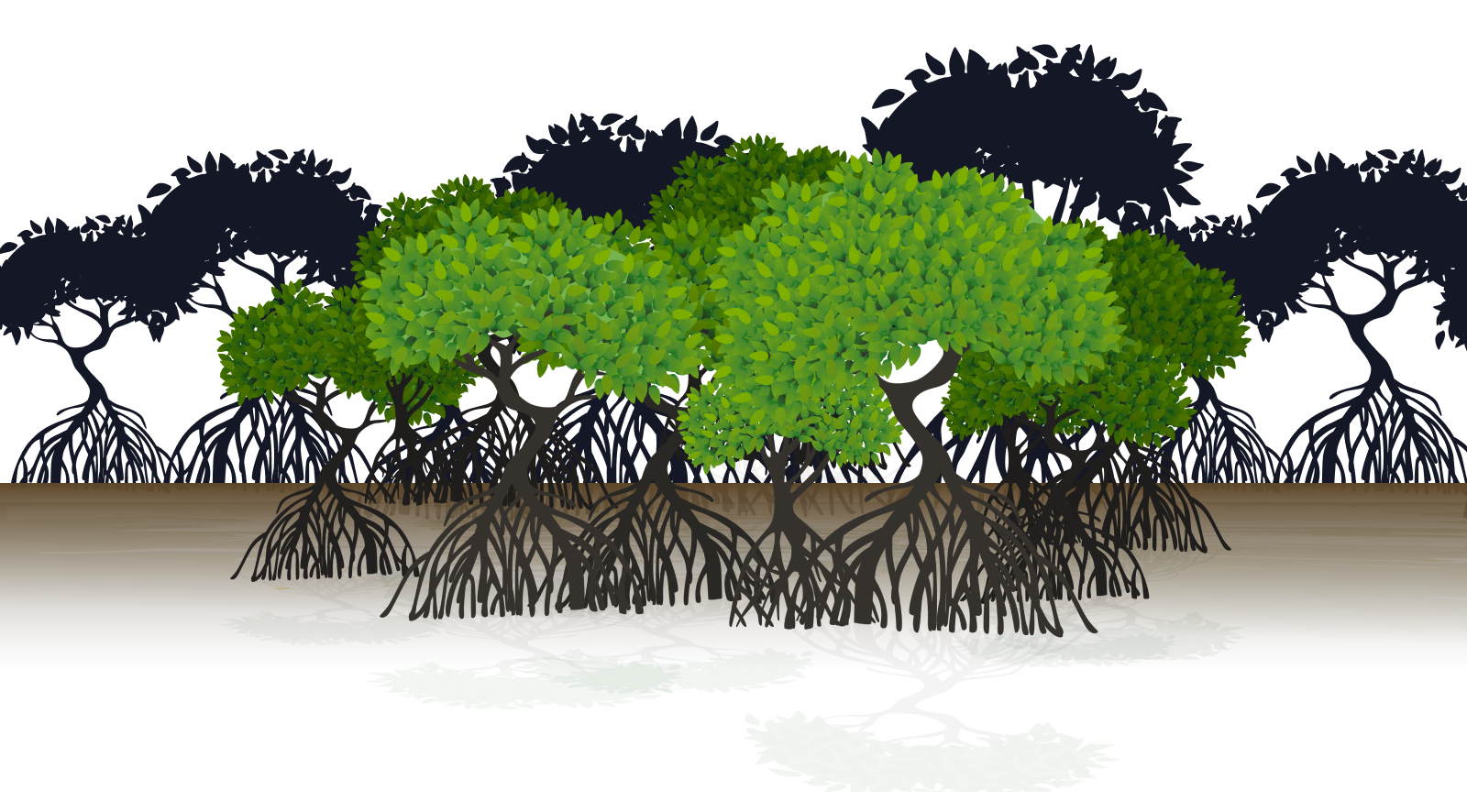
Mangrove
Marine
The marine ecosystem is the largest on Earth. It comprises an astounding variety of plant and animal species such as seagrass, corals, fish, rays, turtles, dugongs, as well as microalgae, plankton, and many more. Their individual existence is interdependent on one another.
For example, a change in ocean temperatures will affect the plant species that can grow there. Animals dependent on these plants for food and shelter will need to adapt to these changes, move to another ecosystem, or perish. Likewise, these changes will have significant consequences for us too.
In this example, we see how the shark plays an important role in ensuring the health of the ocean.
The loss of sharks has led to the decline in coral reefs. Without sharks in the coral reef ecosystem, larger predatory fish, such as groupers, increase in abundance and feed on the herbivores. With less herbivores, macroalgae expands and coral can no longer compete, shifting the ecosystem to one of algae dominance, affecting the survival of the reef system.
Coral reefs are important because they provide habitats and shelter for fish and marine organisms, including reef sharks. The fishing industry depends on coral reefs because they are where fishes spawn and juvenile fish breed before swimming to the open sea. Coral reefs also protect coastlines and vulnerable communities from the damaging effects of wave action and tropical storms.
Mangrove
Forest
Mangroves are considered a natural climate solution with the potential to mitigate climate change - they are three times more effective at storing carbon than terrestrial forests, depositing it in plants and sediment, where it is known as “blue carbon”. They can also hold four times the amount of carbon than the average forest, despite covering only 0.1% of Earth's land surface.
In addition, mangrove ecosystems are among the most productive and biologically diverse ecosystems on the planet. They serve as important habitats for marine life like snappers, sharks, manatees, crabs, and more, which depend on one another for survival.
This example demonstrates how mangroves provide food for reef fishes.
The above example demonstrates how mangroves provide food for reef fishes, which eventually become food for us.
They also are a source of livelihood to millions of people, providing jobs and other resources to communities around the world.
The presence of mangroves on coastlines also offers long term protection to some of the most vulnerable coastal communities from the devastating impacts of hurricanes, storm surges, wave action, and flooding.
Marine
Forest

Watch and read to learn more about biodiversity through these in-depth videos and articles.
Sustainability that starts from within
Why companies must lead the sustainability charge

Natural Climate Solutions
Life on Earth consists of millions of species of plants, animals, insects and micro-organisms, spread across different habitats—from rivers and rainforests to deserts and oceans. This vast variety of life is called biodiversity. ‘Bio’ means life, and ‘diversity’ means variety.
Our world is like a web made up of many strands, each representing the different living species within an ecosystem, all connected together. Forests are homes to animals. Animals consume plants. Bees and other insects help in plant pollination. Plants need healthy soil to grow. Soil is fertilised by fungi that decompose biological matter. Each species, no matter how small, has a role to play in the natural ecosystem and maintaining a planet with a population of more than 7 billion people. When one connection is broken, the whole web becomes more unstable and less resilient.
Biodiversity is fundamental to thriving communities and vital to the well-being of our planet. It is at the heart of Earth’s life-support systems, which we all depend on. Mother Nature’s natural ecosystems and rich biodiversity are crucial in providing us with many wonderful and invaluable things that we take for granted:

A stable supply of food

Clean water

Medicines

A source of oxygen

Economic activity
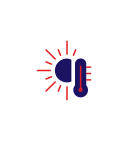
A stable climate

Less natural disasters
.
Over the past 40 years, populations of mammals, birds, fish, reptiles and amphibians have, on average, declined in size by 60 per cent in just over 40 years*, and is expected to drop even further.
Unfortunately, the main reason for this tragic loss of biodiversity is us—the human race. We have cut down forests, released greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, and filled our rivers and oceans with plastic and harmful chemicals.
Irresponsible consumption of resources and unsustainable developments have also destroyed the natural habitats of countless species and consequently accelerated the rate of global warming and worsened the impact of natural disasters. However, while humans may be the cause, we can also definitely be part of the solution.
*Source: Wildlife population has fallen by 60% in just over 40 years. (WWF Living Planet Report, 2018)
Reduce your carbon footprint
What's your carbon footprint? Carbon emissions from your lifestyle choices, such as the transportation you take or the food that you eat, impact the climate.
Find out what your carbon footprint is with Conservation International's calculator and learn how to reduce it today.
Discover how our esteemed clients have developed and implemented business policies and practices
to protect biodiversity and help nature thrive.